Vitamin D
Vitamin D plays a very significant role in disease prevention and maintaining optimal health. Although commonly referred to as a “vitamin” by scientists, vitamin D is actually a steroid hormone that influences as many as 3,000 of the 30,000 genes present in the human body.1 In fact, there are numerous vitamin D receptors located throughout your body.2,3
An estimated 89% of U.S. adults overall, and 91% of U.S. children and teens overall, aren’t getting recommended levels4 of vitamin D.
Vitamin D Disease Incidence Prevention Chart
× ![]()
Click to enlarge or print
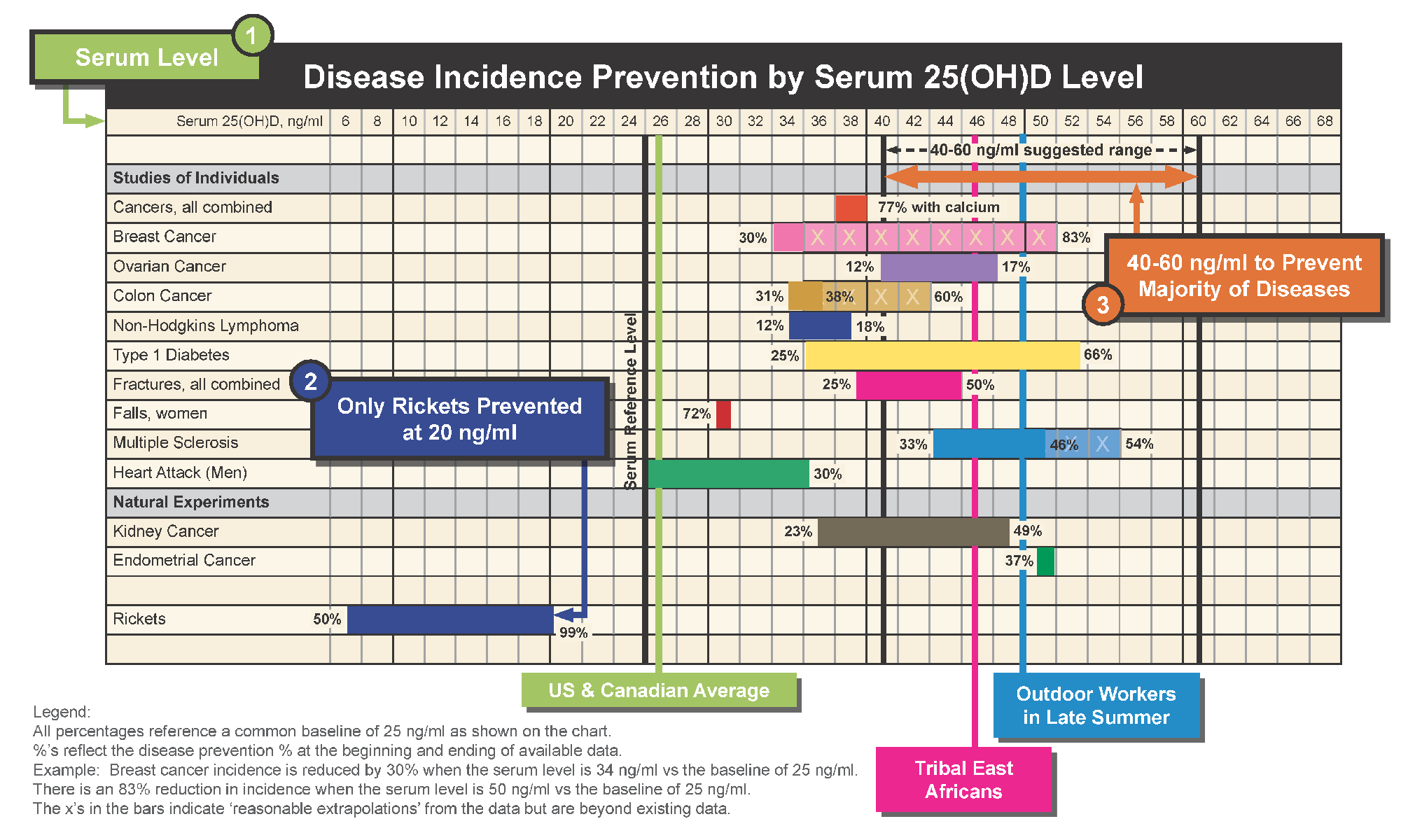
This chart summarizes 15 peer-reviewed research papers about vitamin D and its role in preventing certain cancers, diabetes, fractures and falls, multiple sclerosis and heart attack. Share it with your healthcare practitioner as you determine where you want your vitamin D level to be.
More than just for bone health.
Most people are familiar with vitamin D’s role, along with calcium and phosphorus, in helping to build bones and keep bones strong and healthy. Research also shows that Vitamin D plays a role in muscle function and the immune system.
Vitamin D Disease Incidence Prevention Chart

× ![]()
Click to enlarge or print
This chart summarizes 15 peer-reviewed research papers about vitamin D and its role in preventing certain cancers, diabetes, fractures and falls, multiple sclerosis and heart attack. Share it with your healthcare practitioner as you determine where you want your vitamin D level to be.
Maintaining optimal vitamin D levels may also help slash your risk of cancer by as much as 50-60%, according to several recent studies.5 Vitamin D’s benefits do not stop there. It can help reduce your risk of other conditions, such as chronic inflammation (a risk factor of many chronic diseases), type 2 diabetes, age-related macular degeneration (the leading cause of blindness), and even Alzheimer’s disease.
What’s more, vitamin D has infection-fighting abilities that may be beneficial in the treatment of the common cold and flus, tuberculosis, and pneumonia. Epileptics may also experience better seizure control when they maintain optimal levels of vitamin D.
Sunshine is the main source of vitamin D, but most of us don’t get enough.
Your body makes vitamin D when your skin is exposed to sunlight. People who live in tropical regions do not have any problems acquiring vitamin D, as they get an abundance of sunshine. However, in most of the continental U.S., people do not have sufficient exposure to the sun. It also doesn’t make any sense to expose your skin to the sun when in temperatures lower than 50°F, as you’re getting very scarce amounts of beneficial UVB rays. People who live in most regions in the U.S. (especially those who experience four seasons) are prone to this problem.
Vitamin D Synthesis Likelihood by Month
These charts display the likelihood of vitamin D synthesis across the U.S. per month:
Take note of the times of the year when UVB rays are very minimal where you live. During these times, taking a high-quality vitamin D3 supplement is highly recommended.
The only way to know if you are getting enough vitamin D is to know your levels.
Some people can get enough vitamin D from the sun, their diet or with supplements. But even if you regularly eat a vitamin D-rich diet or take a supplement, your body might not be absorbing the vitamin D.
Vitamin D levels can be measured – by your doctor or at home – using a simple, reliable blood test.
The good news is there is a simple nutritional tool you can have delivered to your home so you can determine whether your vitamin D intake is getting you to the right vitamin D level for your optimal health. Called the 25-hydroxy vitamin D test, it’s the same test used by doctors’ offices and labs and is the most accurate way to measure how much vitamin D in your body.
What will our vitamin D test tell you?
What your vitamin D level is (using the 25-hydroxy vitamin D test, the most accurate way to measure how much vitamin D is in your body).
How your current vitamin D level impacts your health.
How to raise your vitamin D level into the recommended 40-60 mg/ml range.
Enroll in our Omega-3 Index and Vitamin D nutrient field study so you can measure your vitamin D level with our at-home self-test kit. It’s easy and convenient. And you’ll be helping to advance nutrition research and change how health care is delivered.
Know your levels. Join our Omega-3 and Vitamin D nutrient field trial today.
Test your Vitamin D Levels